News
Managing network objects at the command line

If you use Veyon without LDAP/AD integration you always have to configure rooms and computers (in general also referred as network objects) manually. In Veyon 4.0 rooms and computers could only be added one by one using the graphical interface provided by Veyon Configurator. Starting with Veyon 4.1 there are additional possibilities which allow scripted and automated management of network objects.
The new Veyon Control module networkobjects provides commands for adding and removing individual objects, clearing, dumping or listing all objects as well as importing and exporting objects from/to files. Except for import and export all commands are easy to use. Here are a few examples:
veyon-ctl networkobjects clear
veyon-ctl networkobjects add room "Room A"
veyon-ctl networkobjects add computer "Host 1" "host-1.example.org" "aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff" "Room A"
veyon-ctl networkobjects add computer "Host 2" "host-2.example.org" "" "Room A"
veyon-ctl networkobjects remove "Host 0"
veyon-ctl networkobjects remove "f8e9bb69-bd46-4f96-afeb-69e2560dd5c2"
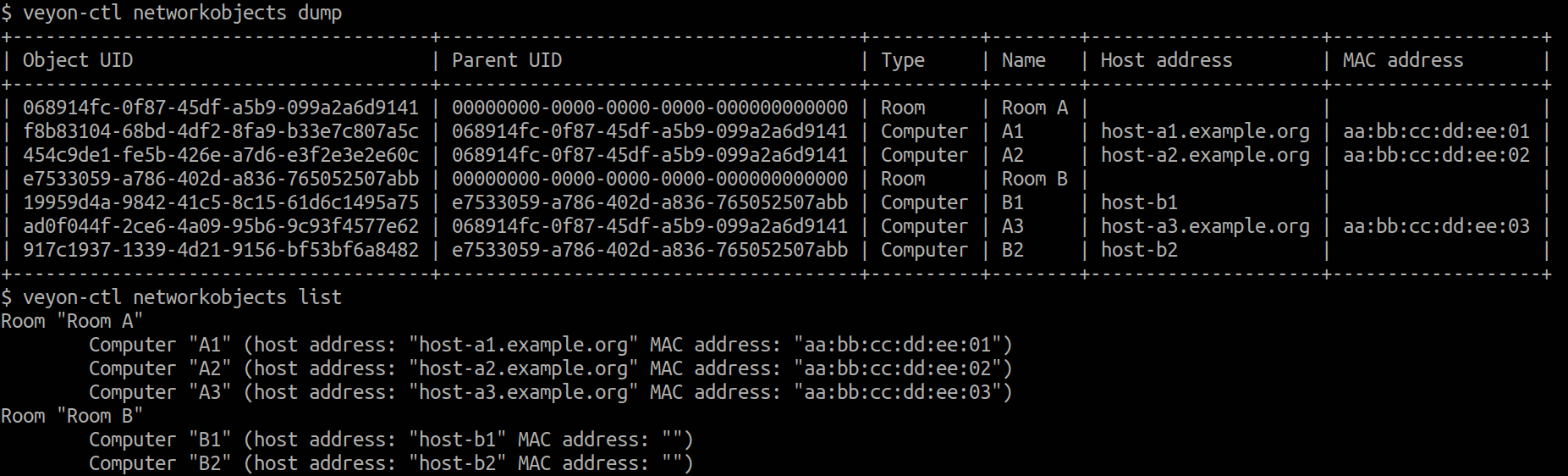
All objects can be dumped or listed using the dump and list commands:
To import objects from text files (e.g. CSV files) you only have to define the format string for parsing the data:
veyon-ctl networkobjects import computers-room-a.csv room "Room A" format "%name%;%host%;%mac%"
veyon-ctl networkobjects import computers-with-rooms.csv format "%room%,%name%,%mac%"
The same syntax can be used for exporting objects:
veyon-ctl networkobjects export all-objects.csv format "%type%;%name%;%host%;%mac%"
veyon-ctl networkobjects export computers-room-a.csv room "Room A" format "%name%;%host%;%mac%"
Advanced users can even specify regular expressions for parsing arbitrarily formatted text files:
veyon-ctl networkobjects import data.txt regex '^"(%room%:[^"]+)";"(%host%:[a-z\\d\\.]+)".*$'
As you can see we added powerful mechanisms for managing network objects in Veyon 4.1. Do you have remarks or suggestions? Don’t hesitate to give feedback through our issue tracker at Github.